- Dalvik Virtual Machine Android free download. software
- Android Os Free Download
- Android Free Download For Pc
- Android software, free download
Alien Dalvik wraps each Android app file in its own virtual machine so it kinda feels as if you were running a native iPad app. The Myriad Group explains: Apr 17, 2018 - Myriad Alien Dalvik 2.0 Download For Ipad. Android Pentesting Course free download. Consists of two components core libraries and dalvik virtual machine so dalvik virtual machine is actually responsible of. Aug 01, 2017 These Android virtual machines are for Windows 7, 8 & 10 and there are easy ways to download the android virtual machine. These can be installed in Virtual box and you can use the apk easily and here is a video tutorial for that.
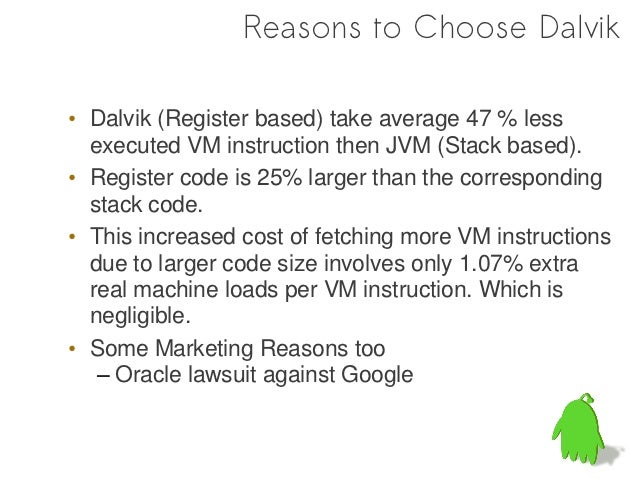
While developing Dalvik Virtual Machine Dan Bornstein and his team realize the constraints specific to the mobile environment which is not going to change in future at least, like battery life, processing power and many more. So they optimized the dalvik virtual machine. Dalvik virtual machine uses register based architecture. The Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) is an android virtual machine optimized for mobile devices. It optimizes the virtual machine for memory, battery life and performance. Dalvik is a name of a town in Iceland. The Dalvik VM was written by Dan Bornstein. The Dex compiler converts the class files into the.dex file that run on the Dalvik VM.
Android Seminar and PPT with pdf report:Android is an operating system designed for the phones, tablets and has taken the mobile internet to a different level. This applied science is widely used by the people and is open source software. Android was established by the android company of California in 2003 by Andy Rubin, the foremost intention of the company was to develop a highly developed system for cameras but later moved towards the smartphones.
In 2005, Google obtained android and revealed in 2007 with the open handset alliance. The android applied science was based on Linux and advanced by Google; it has its own DVM called Dalvik virtual machine which was availed for designing the android application.
Also See: iPad Seminar with report
Android Seminar and PPT with PDF Report
Now, coming to the open handset alliance, it is a companion whose target is to advance open levels for mobile devices and furnish well experience devices for customers at cheaper rates, Android architecture has a group of software's which are divided into four layers and they are:
Capcom collection xbox. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube. Capcom Classics Collection (カプコン・クラシックスコレクション, Kapukon Kurashikkusu Korekushon) is a compilation of arcade games released by Capcom for the PlayStation 2 and Xbox on September 27, 2005 in North America and in 2006 in Japan.
- Application layer
- Application Framework
- Libraries and
- Linux kernel
- Linux Kernel: The bottom layer of the android architecture is the Linux kernel and it genuinely doesn't have the effect on the users, developers and furnishes a standard of separation between device hardware and upper layers of the android software group. The kernel handles all the things that Linux is genuinely better like networking and much more.
- Libraries: Above the Linux kernel, a set of C and C++ library is present and all the sub-components of android operating system use it. Few core libraries are:
- System C library
- SQLite: It retrieves the data or information
- SSL: It furnishes the internet
- SGL: It is a 2D graphics engine
- Libweb core: It is an advanced web browser
- Open GL: It furnishes java interface
- Media Framework: It furnishes unique media code
- Web kit: This is a browser engine
Dalvik Virtual Machine: It is designed only for the android operating system which was advanced by Dan Bornstein; each and every android system runs on its own process called Dalvik virtual machine. It is dependent on Linux kernel for the functions like threading and low-level memory guidance.
- Application Framework: This furnishes many excel standard services to many applications in the context of java classes. Along with it, the framework has the services like:
- Activity Manager: Manage total aspects of the application life cycle and activity group.
- Content Providers: Permits applications to proclaim and share information with other applications.
- Resource Manager: Furnishes admittance to non-code embedded resources.
- Notifications manager: Permits the applications to show alerts and notifications to the users.
- Package Manager: Applications can find the data of other applications through it.
- Telephony Manager: Furnishes the telephone service on the machine.
- Location Manager: It furnishes the admittance to the services and upgrades the change in location.
- Application layer: The topmost layer of the group of software is the application layer and the user mostly interacts with the application layer. Total applications are written using the programming language called java.
About versions of android:
Android is upgrading day by day by including the new features in it and also making the lives more comfortable. Some of the recent versions of android are as follows:
- 0/ 2.1 (Éclair)
- 2 (Froyo)
- 3 (Gingerbread)
- 0 (Honeycomb)
- 1- 4.3 (Jellybean)
- 4 (Kitkat)
- 0 (Lollipop)
- 0 (Marshmallow)
Also See: Google Chrome OS Seminar with Report
Android Security:
In these days all the tasks that were performed in a computer can now be performed on the mobile and this means that you the more virtual information or data in the mobile phones and need to secure it efficiently. Some of the features of the android security are:

- Physical access: It is helpful in preventing hackers by permitting to have unlocked patterns and passwords.
- App permissions: Every app we installed ask our permission to perform any task.
- Application sandbox: This provides the security by not giving one application admittance to the resource of another application.
- Rooting: An application with the root permission can change any part of the android operating system because 'root' is a supreme user standard in Linux.
- Malware: Unfortunately, android has malware issue and this do nothing on non-rooted phones and everything on rooted phones.
Android is now the best operating system for the mobile phones and this not only provides the security features but also enabled us to know about emails, web and much more.
Dalvik Virtual Machine Android free download. software
What development to expect in Android for 2021?
The trends that are going to rule the Android world are mentioned below:
- Beacons Technology
This technology is going to optimize the searching based on the location through Bluetooth signals.
- Wearable Apps
From this, we mean supporting devices like smartwatches for providing solid functionality and design.
- IoT
It provides the business automation that minimizes the manual efforts for making the operations quicker & better.
- 5G Technology
Data transmission will definitely reach new heights with the advent of 5G technology that only offers top speed and gives higher radiofrequency.
Content of the Seminar and pdf report for Android
- Introduction
- What is Android
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Applications
- Architecture
- Future
- Conclusion
- References
Here we are giving you Android Seminar and PPT with PDF report. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it.
Sony acid music studio loops. It was all about Android Seminar and PPT with pdf report. If you liked it then please share it or if you want to ask anything then please hit comment button.
https://studymafia.org/android-seminar-and-ppt-with-pdf-report/Android Seminar and PPT with pdf reportCSE SeminarsAndroid Seminar and PPT with pdf report: Android is an operating system designed for the phones, tablets and has taken the mobile internet to a different level. This applied science is widely used by the people and is open source software. Android was established by the android company of..Sumit ThakurSumitThakursumitsssrt@gmail.comAdministratorI am an Indian Blogger. I am passionate about blogging. If you want to ask me anything about blogging then feel free to ask 🙂Study Mafia: Latest Seminars Topics PPT with PDF Report 2020Dalvik is the name of the Virtual Machine in which Android applications are run. This VM executes Dalvik bytecode, which is compiled from programs written in the Java language. Note that the Dalvik VM is not a Java VM (JVM).
Every Android application runs in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine.
At boot time, a single virtual machine, called 'zygote' is created, which preloads a long list of classes. (As of Android version 2.1 (eclair), the list of classes preloaded by zygote had 1,942 entries). All other 'java' programs or services are forked from this process, and run as their own process (and threads) in their own address space. Both applications and system services in the Android framework are implemented in 'java'.
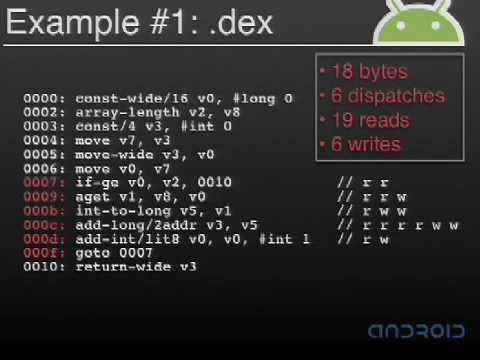
Dalvik was written so that a device can run multiple VMs efficiently. The Dalvik VM executes code in the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format which is optimized for minimal memory footprint. The VM is register-based, and runs classes compiled by a Java language compiler that have been transformed into the .dex format by the included 'dx' tool.
Most Android applications are delivered and stored on the system as packages (.apks), which include both dex bytes code (classes and methods) and resources. During first boot-up the system creates a cache of dex classes in /data/dalvik-cache.
- 6Debugging the VM
Documentation
There is some documentation on Dalvik in the source code in the dalvik/docs directory.See the Android dalvik docs git repository.
The source code has some rather large comments, including near the top of Thread.c and Exception.c. The 'mterp' directory has some notes describing the structure of theinterpreters.
Q&A
From fadden on the android-platform list:
- Who is responsible to read the dex file and call Dalvik ?
- The VM is started by the framework, through the JNI invocation interface. See AndroidRuntime.cpp in frameworks/base/..
- Do you have a tutorial launch an app in the terminal adb: bytecode file > dex file > app launch in Dalvik => and see the result in adb ?
- See 'hello-world.html' in the dalvik/docs directory (linked above).
- Is there a profiler inside Dalvik, which enable us to follow each step in the dalvik execution ?
- You could turn on LOG_INSTR to see each instruction as it is executed. This results in a rather dramatic amount of logging. If you try to do this on a device you will overrun the 64KB kernel log buffer pretty quickly and drop lots of stuff, so it's really only suitable for a 'desktop' build (e.g. sim-eng).
- Also, Dalvik does include instrumentation to allow for tracing and profiling. See http://elinux.org/Android_Tools#traceview
JIT
As of version 2.2 (Froyo), Dalvik includes a Just-In-Time compiler (or JIT).
- See A JIT Compiler for Android's Dalvik VM - video of presentation by Ben Cheng and Bill Buzbee at Google IO, 2010
The Dalvik JIT, as of version 2.2, is a 'trace-granularity JIT', which means that it compiles individual code fragments that it discovers at runtime to be 'hot spots'. (That is, it does notcompile whole methods.) The Dalvik bytecode interpreter is constantly profiling the code it is executing, and when a piece of code is determined to be running a lot, it is passed to a compiler to turn into native code. Several optimizations may be performed in this process. This code is then executed instead of the bytecode, for future runs through this section of the software.
The memory overhead of the JIT is reported to be between 100K to 200K per application.The ratio of code size between native instructions and DEX byte codes in one example give (see slide 22 of the presentation) was 7.7 to 1. That is, native instructions take approximately 8 times as much space as DEX byte codes do to perform the same operations.
Relationship to Java
Because Dalvik is not referred to as a Java Virtual Machine it does not utilize the branding of 'Java'. Also, it does not execute Java bytecodes. Hence, Google can ignore licensing issues withSun or Oracle, with regards to Java.
However, a Java compiler and set of class libraries are required in order to create a Dalvik program.
Android Os Free Download
As of March 2010, only the Sun JDK, version 1.5 is supported for building the Android system and add-on Android applications.
Dalvik on other platforms
- Myriad Alien Dalvik - an implementation of the Dalvik VM for other platforms (demonstrated first on Meego)
Debugging the VM
There are a number of properties you can set, to control operation of the VM and allow for debugging various aspectsof the system:
See http://netmite.com/android/mydroid/dalvik/docs/embedded-vm-control.html
(Note that this is in /dalvik/docs, along with a whole bunch of other fileswith information about Dalvik.)
this mentions a number of features you can control with properties, including:
- checkjni - various checks when JNI is used
- enableassertions - enable assertions in the VM code
- verify-bytecode - whether to perform bytecode verification
- execution-mode - whether to use optimized assembly or portable C code for the interpreter
- stack-trace-file - where to put stack trace data when a SIGQUIT is received
Getting stack traces
You can force the VM to dump a stack trace of all threads by sending a SIGQUIT signal. This can be done using 'kill -3 ', where pid in the main dalvik process. By default, the stack trace goes to the android log,but you can have the data sent to a file (using the dalvik.vm.stack-trace-file property) instead.
Using checkJNI
CheckJNI refers to a special runtime mode of the Dalvik VM, which forces the VM to run certain checkand report problems when it sees certain errors occuring from code called via JNI.
See http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/07/debugging-android-jni-with-checkjni.html
Resources
- Dalvik VM Internals - video of presentation by Dan Bornstein at Google IO, 2008
Android Free Download For Pc
- DEX file format, reverse engineered by Michael Pavone
- Application layer: The topmost layer of the group of software is the application layer and the user mostly interacts with the application layer. Total applications are written using the programming language called java.
About versions of android:
Android is upgrading day by day by including the new features in it and also making the lives more comfortable. Some of the recent versions of android are as follows:
- 0/ 2.1 (Éclair)
- 2 (Froyo)
- 3 (Gingerbread)
- 0 (Honeycomb)
- 1- 4.3 (Jellybean)
- 4 (Kitkat)
- 0 (Lollipop)
- 0 (Marshmallow)
Also See: Google Chrome OS Seminar with Report
Android Security:
In these days all the tasks that were performed in a computer can now be performed on the mobile and this means that you the more virtual information or data in the mobile phones and need to secure it efficiently. Some of the features of the android security are:
- Physical access: It is helpful in preventing hackers by permitting to have unlocked patterns and passwords.
- App permissions: Every app we installed ask our permission to perform any task.
- Application sandbox: This provides the security by not giving one application admittance to the resource of another application.
- Rooting: An application with the root permission can change any part of the android operating system because 'root' is a supreme user standard in Linux.
- Malware: Unfortunately, android has malware issue and this do nothing on non-rooted phones and everything on rooted phones.
Android is now the best operating system for the mobile phones and this not only provides the security features but also enabled us to know about emails, web and much more.
Dalvik Virtual Machine Android free download. software
What development to expect in Android for 2021?
The trends that are going to rule the Android world are mentioned below:
- Beacons Technology
This technology is going to optimize the searching based on the location through Bluetooth signals.
- Wearable Apps
From this, we mean supporting devices like smartwatches for providing solid functionality and design.
- IoT
It provides the business automation that minimizes the manual efforts for making the operations quicker & better.
- 5G Technology
Data transmission will definitely reach new heights with the advent of 5G technology that only offers top speed and gives higher radiofrequency.
Content of the Seminar and pdf report for Android
- Introduction
- What is Android
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Applications
- Architecture
- Future
- Conclusion
- References
Here we are giving you Android Seminar and PPT with PDF report. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it.
Sony acid music studio loops. It was all about Android Seminar and PPT with pdf report. If you liked it then please share it or if you want to ask anything then please hit comment button.
https://studymafia.org/android-seminar-and-ppt-with-pdf-report/Android Seminar and PPT with pdf reportCSE SeminarsAndroid Seminar and PPT with pdf report: Android is an operating system designed for the phones, tablets and has taken the mobile internet to a different level. This applied science is widely used by the people and is open source software. Android was established by the android company of..Sumit ThakurSumitThakursumitsssrt@gmail.comAdministratorI am an Indian Blogger. I am passionate about blogging. If you want to ask me anything about blogging then feel free to ask 🙂Study Mafia: Latest Seminars Topics PPT with PDF Report 2020Dalvik is the name of the Virtual Machine in which Android applications are run. This VM executes Dalvik bytecode, which is compiled from programs written in the Java language. Note that the Dalvik VM is not a Java VM (JVM).
Every Android application runs in its own process, with its own instance of the Dalvik virtual machine.
At boot time, a single virtual machine, called 'zygote' is created, which preloads a long list of classes. (As of Android version 2.1 (eclair), the list of classes preloaded by zygote had 1,942 entries). All other 'java' programs or services are forked from this process, and run as their own process (and threads) in their own address space. Both applications and system services in the Android framework are implemented in 'java'.
Dalvik was written so that a device can run multiple VMs efficiently. The Dalvik VM executes code in the Dalvik Executable (.dex) format which is optimized for minimal memory footprint. The VM is register-based, and runs classes compiled by a Java language compiler that have been transformed into the .dex format by the included 'dx' tool.
Most Android applications are delivered and stored on the system as packages (.apks), which include both dex bytes code (classes and methods) and resources. During first boot-up the system creates a cache of dex classes in /data/dalvik-cache.
- 6Debugging the VM
Documentation
There is some documentation on Dalvik in the source code in the dalvik/docs directory.See the Android dalvik docs git repository.
The source code has some rather large comments, including near the top of Thread.c and Exception.c. The 'mterp' directory has some notes describing the structure of theinterpreters.
Q&A
From fadden on the android-platform list:
- Who is responsible to read the dex file and call Dalvik ?
- The VM is started by the framework, through the JNI invocation interface. See AndroidRuntime.cpp in frameworks/base/..
- Do you have a tutorial launch an app in the terminal adb: bytecode file > dex file > app launch in Dalvik => and see the result in adb ?
- See 'hello-world.html' in the dalvik/docs directory (linked above).
- Is there a profiler inside Dalvik, which enable us to follow each step in the dalvik execution ?
- You could turn on LOG_INSTR to see each instruction as it is executed. This results in a rather dramatic amount of logging. If you try to do this on a device you will overrun the 64KB kernel log buffer pretty quickly and drop lots of stuff, so it's really only suitable for a 'desktop' build (e.g. sim-eng).
- Also, Dalvik does include instrumentation to allow for tracing and profiling. See http://elinux.org/Android_Tools#traceview
JIT
As of version 2.2 (Froyo), Dalvik includes a Just-In-Time compiler (or JIT).
- See A JIT Compiler for Android's Dalvik VM - video of presentation by Ben Cheng and Bill Buzbee at Google IO, 2010
The Dalvik JIT, as of version 2.2, is a 'trace-granularity JIT', which means that it compiles individual code fragments that it discovers at runtime to be 'hot spots'. (That is, it does notcompile whole methods.) The Dalvik bytecode interpreter is constantly profiling the code it is executing, and when a piece of code is determined to be running a lot, it is passed to a compiler to turn into native code. Several optimizations may be performed in this process. This code is then executed instead of the bytecode, for future runs through this section of the software.
The memory overhead of the JIT is reported to be between 100K to 200K per application.The ratio of code size between native instructions and DEX byte codes in one example give (see slide 22 of the presentation) was 7.7 to 1. That is, native instructions take approximately 8 times as much space as DEX byte codes do to perform the same operations.
Relationship to Java
Because Dalvik is not referred to as a Java Virtual Machine it does not utilize the branding of 'Java'. Also, it does not execute Java bytecodes. Hence, Google can ignore licensing issues withSun or Oracle, with regards to Java.
However, a Java compiler and set of class libraries are required in order to create a Dalvik program.
Android Os Free Download
As of March 2010, only the Sun JDK, version 1.5 is supported for building the Android system and add-on Android applications.
Dalvik on other platforms
- Myriad Alien Dalvik - an implementation of the Dalvik VM for other platforms (demonstrated first on Meego)
Debugging the VM
There are a number of properties you can set, to control operation of the VM and allow for debugging various aspectsof the system:
See http://netmite.com/android/mydroid/dalvik/docs/embedded-vm-control.html
(Note that this is in /dalvik/docs, along with a whole bunch of other fileswith information about Dalvik.)
this mentions a number of features you can control with properties, including:
- checkjni - various checks when JNI is used
- enableassertions - enable assertions in the VM code
- verify-bytecode - whether to perform bytecode verification
- execution-mode - whether to use optimized assembly or portable C code for the interpreter
- stack-trace-file - where to put stack trace data when a SIGQUIT is received
Getting stack traces
You can force the VM to dump a stack trace of all threads by sending a SIGQUIT signal. This can be done using 'kill -3 ', where pid in the main dalvik process. By default, the stack trace goes to the android log,but you can have the data sent to a file (using the dalvik.vm.stack-trace-file property) instead.
Using checkJNI
CheckJNI refers to a special runtime mode of the Dalvik VM, which forces the VM to run certain checkand report problems when it sees certain errors occuring from code called via JNI.
See http://android-developers.blogspot.com/2011/07/debugging-android-jni-with-checkjni.html
Resources
- Dalvik VM Internals - video of presentation by Dan Bornstein at Google IO, 2008
Android Free Download For Pc
- DEX file format, reverse engineered by Michael Pavone
